Plants develop their pigmentation (colors) in nature in order to protect themselves from harmful UV radiation from the sun and other environmental stressors. These adaptive qualities help them to survive and procreate. When we consume these compounds (known as anthocyanins), they give us powerful antioxidant protection that helps us deal with stress, radiation, and environmental toxins. These antioxidants are categorized as polyphenols and consuming them is one of our best strategies for preventing cancer.
How Anthocyanins Help Protect You from Cancer
Skin damage is most often caused as a result of injury from free radicals. Abnormalities in cell structure not only lead to aging… they can cause cancer as well. Chronic exposure to oxidative stress in cell signaling processes promotes the formation of genetic mutations that replicate abnormally… which can lead to cancer.
Here are 4 ways anthocyanin antioxidants protect you against cancer development.
1 | Natural SPF Protection
The name anthocyanin is derived from “cyan” in Greek which means dark blue. The deep blue and purple colors of anthocyanins are created at the cellular level and provide sun protection by absorbing blue-green light and UV rays in plants. These antioxidant components significantly inhibit stress on the plant and also scavenge free radicals for additional protective capabilities.
There are more than 600 types of naturally occurring anthocyanins. The most common form, Cyaniding-3-glucoside (C3G), has been found to directly influence gene expression. Clinical studies have shown that C3G improves the activity of protective genes and suppresses those that cause inflammation and other tumor-promoting activities.
2 |Reduce Inflammation
Various factors contribute to the chronic inflammation which afflicts the majority of people today. Depleted antioxidants, nutrient deficiencies, increased free radical formation, poor fatty acid concentrations, increased toxic accumulation, as well as persistent emotional, mental, physical, and neurological stress all exacerbate the inflammatory damage to our cells and tissue.
Inflammation stimulates cellular activity that promotes cancer-inducing oncogenes. Oncogenes cause cancer cells to replicate and are major contributors to cancer metastasizing into neighboring regions. Anthocyanins are shown to control inflammatory conditions by activating a “cell suicide” pathway in cancer cells known as apoptosis. Apoptosis is a natural defense system in the body designed for several purposes. Most importantly, in the case of cancer cells, apoptosis helps prevent damage from occurring inside our tissue.
Tumor grade is an indicator of how quickly a tumor is likely to grow and spread. If the tumor cells are well organized, the tumor is considered “well-differentiated.” These tumors tend to grow and spread at a slower rate than less organized or “undifferentiated” tumor cells. C3G has shown the ability to promote differentiation in certain cancers, such as melanoma.
3 | Improve Metabolic Pathways
Cancer is considered a metabolic disease which thrives off of altered forms of energy. C3G improves the metabolic pathways involved in regulating glucose and may limit the occurrence of altered energy forms which feed cancer growth. The availability of anthocyanins in our diets is far greater than many other potent antioxidants and thus is a readily accessible tool to prevent cancer. In fact, C3G extract is suggested to have potent chemotherapeutic potential against colorectal cancer. C3G has also been shown to effectively reduce free fatty acids associated with obesity and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetics.
4 | Turn on Cancer Cell Apoptosis
That the same oncogenes previously described can limit inflammation and turn on apoptotic pathways in cancer cells is perhaps one of the greatest realizations in our understanding of malignant cancers. Genetic mutations which alter these oncogenes lead to faulty signaling which initiates rather than suppresses cancer.
Anthocyanins protect oncogenes from toxic agents which disrupt healing responsibilities. The ability for any compound to have such a profound impact on apoptosis in abnormal cells is conclusively one of the best therapeutic strategies to prevent and heal from the effects of cancer.
Natural extracts containing anthocyanins have been demonstrated to inhibit mutagenic expression of cancer related to the colon and rectum, prostate, and esophagus.
A Summary of Anthocyanin Characteristics:
- Create pigmentation in dark colored fruits and vegetables
- Natural SPF protectant for both plants and our skin
- Scavenge free radicals
- Reduce inflammatory markers
- Suppress cytokine activity
- Trigger activity in cells and genes that protect against inflammation and shut off the communication signals which promote expression of oncogenes
- Promote normal cell differentiation of certain cancers
- Increase apoptosis in cancer cells
Equipping the body with these antioxidants is critical to combating the constant flow of toxins and hazardous activity that ages and damages the human body. Foods containing anthocyanins have been traditionally used in herbal medicine to treat infections, liver disorders, high blood pressure, and even the common cold. The ability for anthocyanins to improve blood circulation is one possible reason why anthocyanins have such anti-inflammatory and anti-carcinogenic effects.
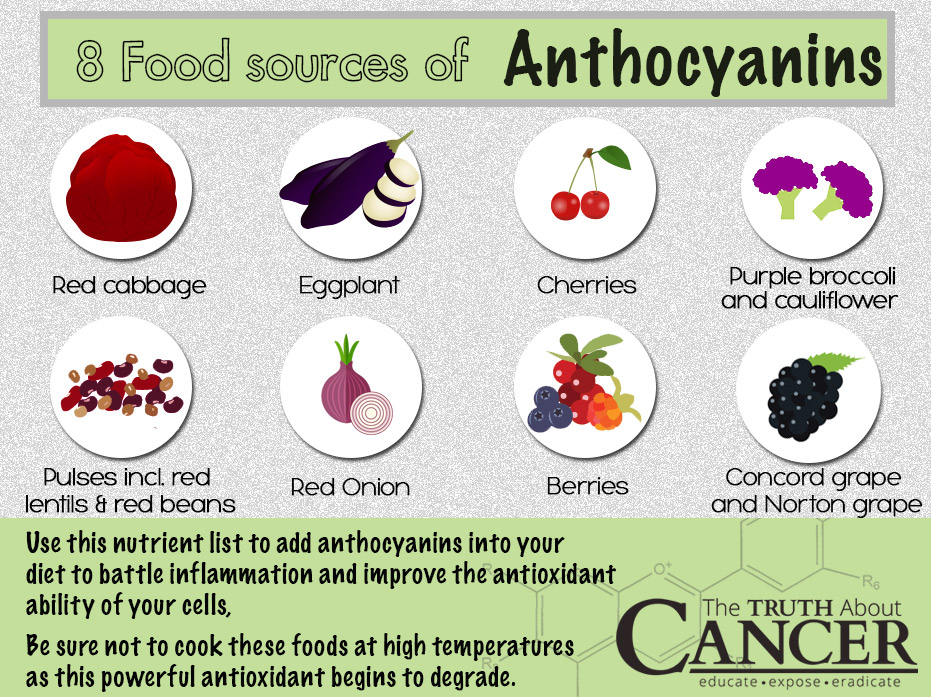
What Foods Contain Anthocyanins?
Adding a variety of natural colors into your diet can not only help you battle inflammation and improve the antioxidant ability of your cells, but it will also significantly impact your body’s ability to prevent cancer. Use this nutrient list to add more anthocyanins into your diet. Be sure not to cook these foods at high temperatures as this powerful antioxidant begins to degrade.
- Cherries
- Purple cauliflower, red cabbage, and purple broccoli
- Red onion
- Eggplant
- Pulses including red lentils and red beans
- Berries including wild blueberries, black raspberries, marion blackberries, black currants, acai, red currants, strawberries, goji berries, and aronia (also known as chokeberries)
- Grapes such the common concord grape and Norton grape
- Sweet potato
Incorporating Anthocyanins into Your Diet
There are a variety of ways you can add anthocyanins into your diet. You can start your day by preparing a mix of your favorite berries to enjoy with your breakfast. Red cabbage is an excellent addition to sauerkraut or can be juiced. Try sautéing or steaming red cabbage, purple cauliflower, purple broccoli, and purple (non-GMO) corn with grass-fed butter and herbs for amazing cancer preventative benefits.
Adding blueberries, blackberries, and raspberries to your smoothies each day is an easy and tasty way to get more anthocyanins. Bilberries, commonly found as dried fruit, in an extracted powder or in supplemental form also exhibit anti-mutagenic potential.
The research into anthocyanin benefits is promising for anti-cancer therapies because regardless of the availability of fresh berries throughout the year, dried forms can be just as advantageous as a cancer-prevention tool. Patients with colorectal cancer particularly benefit from berry consumption.
Article Summary
Plants develop their pigmentation (colors) in nature in order to protect themselves from harmful UV radiation from the sun and other environmental stressors.
When we consume these compounds (known an anthocyanins), they give us powerful antioxidant protection and are one of our best strategies for preventing cancer.
Here are 4 ways anthocyanin antioxidants protect you against developing cancer:
- Natural SPF Protection
- Reduce Inflammation
- Improve Metabolic Pathways
- Turn On Cancer Cell Apoptosis (cell suicide)
Equipping the body with these antioxidants is critical to combating the constant flow of toxins and hazardous activity that ages and damages the human body.
Foods containing anthocyanins have been traditionally used in herbal medicine to treat infections, liver disorders, high blood pressure, as well as the common cold.
Here are some foods that are good sources of anthocyanins. Do not overcook them as it will cause the antioxidants to degrade.
- Cherries
- Purple cauliflower, red cabbage, and purple broccoli
- Red onion
- Eggplant
- Pulses including red lentils and red beans
- Berries including wild blueberries, black raspberries, marion blackberries, black currants, acai, red currants, strawberries, goji berries, and aronia (also known as chokeberries)
- Grapes such the common concord grape and Norton grape
- Sweet potato



















My husband has cancer and he is 88 yrs of age. It is prostate cancer and he is seemingly in his last stage. He has lost weight. I wish there was a cure.